Administration
The Graduate Program in Administration (PPAD) at the Pontifical Catholic University of Paraná (PUCPR) School of Business offers master’s and doctoral programs, promoting excellence in terms of the highest-level education for professors and researchers. Recommended with a rating of 5 by Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), the Program has been consolidated as one of the best administration programs in the country.
The achievement of a rating of 5 brought national fame to the Program, which resulted in its more significant interaction with other Graduate Programs in the country, helping its consolidation as one of the preeminent programs in the area. Internationally, its performance has increased the participation of foreign candidates in the selection process. These candidates come from several countries, especially from Latin America and the United States; the Program also has agreements with other institutions worldwide. Given the importance of research in social and business development, the Graduate Program in Administration at the PUCPR School of Business, through a current proposal, has encouraged applied research aiming to contribute to the theory, the areas of strategy and administration, and the companies surveyed. Thus, the Program offers a wide association between scientific research and business practices.
Goals
The primary goal of the Program is to train professors and researchers who excel in conducting scientific research in administration, contributing to the area’s theoretical development without losing sight of its applicability to the organizational context, and its social impact.
History
In 2000, the Graduate Program in Administration began, offering a master’s degree in administration. On September 22, 2000, the Coordination recommended it for the CAPES. It was also recognized by the Ministry of Education on September 4, 2002, by Ordinance no. 2,530.
In recent years, in response to the market, several higher education institutions in Paraná and, especially, in the Metropolitan Region of Curitiba, have installed or expanded their activities. Thus, there was an increasing demand for master’s programs, due to the need to improve the faculty qualifications of these institutions.
There was only one academic master’s program meeting this demand in Curitiba, the one from the Federal University of Paraná (UFPR), which offered only few annual placements. This made PUCPR realize the importance of creating a master’s program in administration to improve the demand and provide an opportunity for researchers in the area who already worked at the Institution to develop their research, being linked to a formally established Program.
During the 2001–2003 triennium evaluation conducted by CAPES, the Master’s Program in Administration at PPAD/PUCPR achieved a rating of 5. In 2006, the doctoral administration program obtained a recommendation from CAPES, with a rating of 4. In 2007, in CAPES’ triennial evaluation, the doctoral program also achieved a rating of 5.
Strategic Administration
The PPAD’s area of concentration is strategic administration.
In 2017, in response to the economic changes in the State and society, the PPAD restructured its areas and research groups, but maintained its concentration area. Three areas were created to replace the previous ones: strategy in organizations, Strategic finance, and marketing Strategies. Each of these areas is divided into research groups, with two groups in marketing (consumer behavior and digital marketing), two in finance (corporate finance and behavioral finance), and four in strategy in organizations (strategy and competitiveness, organizational complexity, organizational studies, and innovation and sustainability).
The Master’s and Doctoral Programs in Administration at PUCPR conduct research in three areas:
- strategy in organizations;
- marketing strategies;
- strategic finance.
The sub-areas and research groups of each area in the Program are presented below.
Description of the Research Groups in the Strategy in Organizations Area.
Research Area
Strategy in Organizations
- Strategy in Organizations
The GIS aims to conduct research in innovation management (IM), knowledge management (KM), and sustainability in organizations, both in public and private organizations. Specific topics include open innovation; social innovation; social management; innovation ecosystems; KM practices, innovativeness, sustainability indicators; eco-efficiency; eco-innovation; sustainable universities, sustainable supply chain management, sustainable products, and reverse logistics.
PPAD faculty members in this group:
- Carlos Olavo Quandt
- June Alisson Westarb Cruz
- Ubiratã Tortato (leader)
- Carlos Olavo Quandt
- June Alisson Westarb Cruz
- Ubiratã Tortato
- Complexity and Organizational Management
COGEO’s primary goal is to foster research focusing on problems that make the management of complex and pluralist organizations challenging. By their nature, these organizations present behavior not yet explained by the traditional rational theories still prevalent in the literature. Therefore, studies based on complexity theories and organizational theory are prioritized, focusing on complex systems characterized by nonlinearity, self-organization, emergence, uncertainty, and unpredictability. Studies by this group also focus on problems arising from management practices imported from the business sector, which are applied to complex systems whose results have produced inefficiency, wasted resources, disappointment, and frustration.
PPAD faculty members in this group:
- Victor Meyer Jr (leader)
- Jansen Maia Del Corso
- Paulo Mussi Augusto
- Strategy and Competitiveness (GPEC)
The GPEC research group aims to conduct research, studies, and discussions that encompass a wide diversity of dimensions in the field of strategy and competitiveness. For its research, the group uses various research frameworks, research methods, and qualitative and quantitative data techniques.
PPAD faculty members in this group:
- Eduardo Damião da Silva (leader)
- Heitor Takashi Kato
- Jansen Maia Del Corso
- Bruno Henrique Rocha Fernandes
- Carlos Olavo Quandt
- Organizational Studies (GPEO)
The GPEO research group aims to conduct investigations supported by a wide range of theories, especially those in the social sciences. The group’s scientific research fits in two main branches of organizational studies: theory of organizations, a perspective of macro bias, and organizational behavior, a micro perspective in organizational studies. These areas are investigated in business, religious, union, public, or cultural organizations. The group is also characterized by epistemological diversity and various methods and techniques for processing qualitative and quantitative research data in its investigations. The group’s work system is focused on the support and continuous evaluation of the scientific research of its participants. This process materializes through seminars, workshops, and biweekly meetings, where articles, dissertations, and theses, are presented and discussed, from the seminal phase to the final report.
Research Area
Marketing
The marketing area is divided into two research groups:
- i) Consumer behavior and marketing strategies
- ii) Digital marketing.
- 2.1 Consumer Behavior and Marketing Strategies
The study group focuses on consumer reaction patterns to new technologies, the relationships between consumers and companies or brands, communication effect on information processing by consumers, retail and services, and strategic value-based marketing relationships. To understand these multifaceted phenomena with qualitative and quantitative approaches and mixed methods that best suit the investigated problems, theories from economics, mathematics, sociology, psychology, and anthropology are used.
PPAD faculty members in this group:
- Eliane Francisco Maffezzolli
- Heitor Takashi Kato
- Paulo de Paula Baptista (leader)
- Renato Zancan Marchetti
- Juan José Camou Viacava
- 2.2 Digital Marketing (GMKTD)
In the scope of the digital marketing group’s investigations are phenomena arising from the intensification in the use of the Internet, mobile telephony (SMS and smartphones), interactive television, and data digitization. These include consumer behavior on the internet’s social networks (mainly Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube), digital engagement, and mapping influence profiles; new communication tools, SEO (search engine optimization), SEM (search engine marketing), Google Analytics and KPIs (key performance indicators) for digital campaigns; the Internet of Things; mobile marketing; and big data. The group uses a multidisciplinary approach that involves different references in communications, psychology, sociology, computer science, business, and the like.
PPAD faculty members in this group:
- Eliane Francisco (leader)
- Heitor Kato
- Paulo Baptista
- Renato Marchetti
- Juan José Camou Viacava
Research Area
Finance
The finance area is divided into two research groups: corporate finance and behavioral finance.
- 3.1 Corporate Finance (GPFIN)
The GPFIN group is dedicated to studying the strategic financial management of organizations. The studies conducted in this group seek to understand the management of financial resources for decision-making and optimization of organizational resources based on the achievement of public and private institutions’ strategic goals. Among the topics of interest to this group, we highlight companies’ capital structure, cost management and investment analysis, capital budgets, the financial and capital markets, risk management and asset pricing, and the economy of a given sector. These types of studies are characterized by the use of predominantly quantitative research techniques, through multi-criteria analysis, modeling, econometrics, and other statistical analyses.
PPAD faculty members
- Alceu Souza
- Angela Cristiane Santos Póvoa
- June Alisson Westarb Cruz
- Pedro Guilherme Piccoli (leader)
- 3.2 Behavioral Finance
The behavioral finance research group (GPFIN-Behavioral) aims to conduct research based on modern theories in economics, psychology, sociology, and administration. Among the most recurring topics are heuristics and cognitive biases, with emphasis on the effects of anchoring, endowment, representativeness, priming, and availability. More recently, experimental game theory and its applications to administration have also been studied by this group. Investigations are guided by diverse methodological approaches, both quantitative and qualitative, with frequent field or laboratory experiments.
PPAD faculty members
- Alceu Souza
- Angela Cristiane Santos Póvoa (leader)
- Pedro Guilherme Piccoli
The original text here is difficult to understand. I have edited it to the best of my understanding.
All students in the Business master’s program have direct access to the internet and the right to remote access to the local network at the PUCPR. With two large auditoriums, the Central Library at the Curitiba Campus has space for studying and for cultural events.
Currently, in addition to traditional (printed) media, the library has modern information devices—such as electronic databases, Internet, cable television, and video—and individual study rooms. The library’s collection comprises approximately 140,000 books, with approximately 3,600 titles and 10,000 copies of works in administration.
The PUCPR libraries also hold copies of national and international journals and articles on topics covered in the master’s program’s main administration subjects. The library collection can be accessed online through the local PUCPR network. The library provides access to the following electronic databases: EBSCO, Francis, Pascal, Academic Search Elite, Expanded Academic Educational Full Text, Humanities Full Text, Social Science Full Text, and General Periodicals on Disc, and Dissertations – Proquest.
In addition, PUCPR maintains institutional exchange agreements with several national and international universities and research institutes.
The GPL strongly invests in internationalization. Some of the several internationalization actions are:
Partnerships with foreign universities
The GPL-PUCPR has several partnerships with foreign universities, enabling the development of cooperation research activities, international events, exchange of master and doctoral students, co-supervision of thesis and dissertations, joint publications, among other activities. Some of the main current partnerships are:
- Paris I Panthéon-Sorbonne University (France)
- University of Lisbon (Portugal)
- University of Connecticut (United States)
- Rovira i Virgili University (Spain)
- Portuguese Catholic University (Portugal)
- Externado University of Colombia (Colombia)
- University of Rosario (Colombia)
- National University of the Litoral (Argentina)
International research networks
GPL professors and students actively participate in international Research Groups, Networks, and Institutes. Professors participate in master’s and doctorate examination boards abroad through the joint activities developed in these networks. Some of the main international research networks in which the GPL-PUCPR participates are:
- Euro-Latin American Teaching Network of Administrative Law (www.redoeda.com)
- Inter-American Network of Fundamental Directorates and Democracy (https://red-idd.com/)
- Law Network, class struggle and reconfiguration of capital (https://aneicj.org/gt-clacso-derecho-clases-reconfiguracion-del-capital/)
- IUCN Academy of Environmental Law (https://www.iucn.org)
- World Complexity Science Academy (https://www.wcsaglobal.org/)
Reception of foreign visiting professors at PUCPR
The GPL-PUCPR receives two to three foreign professors every year, who stay at least 30 days on the program, teaching elective courses in English or Spanish to master’s and doctoral students, participating in thesis and dissertation project discussion meetings, offering extension courses open to undergraduate students, and giving lectures.
Working as Visiting Professors at foreign universities
GPL-PUCPR professors often work in foreign universities as visiting professors, offering master’s and doctorate courses, co-supervising thesis and dissertations, and participating in academic activities. The main participations in the 2017-2020 period were at the Paris I Panthéon-Sorbonne University (France), Externado de Colombia University (Colombia), Autonomous University of San Luis Potosí (Mexico) and National University of the Litoral (Argentina).
Post-Doctorate program abroad
GPL-PUCPR professors often conduct postdoctoral research at foreign universities, most of them supported by CAPES grants. From 2017-2020, post-doctoral research was conducted at the Paris I Panthéon-Sorbonne University (France), the University of California (USA), and the University of Coimbra (Portugal).
Foreign Language Courses (PUCPR Global Classes)
The university offers the PUCPR Global Classes Program, where undergraduate and graduate courses are taught in another language at three different foreign language proficiencies. The GPL-PUCPR offers master’s and doctorate programs in English and Spanish at levels 1, 2, and 3.
Doctorate, Sandwich Doctorate, and Sandwich Master Co-supervision
The GPL-PUCPR has PhD students developing dissertations under co-supervision (double degree) with foreign universities such as the Paris I Panthéon-Sorbonne University (France), the Rovira I Virgili University (Spain), the Portuguese Catholic University (Portugal), and the National University of Colombia (Colombia). Several doctoral students attend sandwich doctoral periods at foreign universities every year, with CAPES and CNPq grants, either through a partnership already formalized or through new partner research initiatives. Master’s students also take sandwich periods at foreign universities, acquiring part of affiliated institutions’ credits.
Double Degree Program
The GPL-PUCPR offers a Double Degree Program with the University of Connecticut (USA), which allows master’s and PhD students to attend part of the credits at PUCPR, part at UConn, have their thesis and dissertations written in English and co-supervised by both a PUCPR and a UConn professor and, in the end, obtain GPL-PUCPR and UConn LL.M titles.
Foreign students and researchers in the GPL-PUCPR
The GPL PPGD annually receives master’s and PhD students from several countries (such as Colombia, Angola, and Senegal), who integrate into the program and interact with Brazilian students, and students who come for research periods (foreigners in a sandwich doctorate in Brazil). The GPL also receives foreign PhDs in postdoctoral research internships from countries such as Spain and Egypt.
Professors and students participation in international congresses
GPL professors attend to several international congresses abroad, together with their foreign research partners. The participation of master’s and PhD students is encouraged, through institutional policies of full funding for professors and students’ participation in international congresses (covering transport, accommodation and registration fees).
Organization of congresses, conferences and international courses at PUCPR
The GPL-PUCPR organizes, throughout each year, dozens of research and extension events with foreign professors at PUCPR, with open participation to the undergraduate and graduate community, as well as to the external community.
Research funding by international agencies
The GPL-PUCPR has research projects funded by international promotion agencies, such as the Ford Foundation, which in the 2017-2020 quadrennium supported projects such as the “Observatory of Consultation Protocols” (related to Convention 169 of the International Labor Organization).
International Publications
The GPL-PUCPR faculty frequently publishes scientific articles in foreign legal journals well qualified in Qualis (A1 and A2), having publications in journals of international impact according to the Scimago Journal Rank (Q1). There are also scientific articles in co-authorship with foreign researchers (international collaboration) and collective works coordinated in partnership with foreign professors (Spain, France, and India), published in Brazil and abroad.
Internationalization Board and PUC Idiomas (Languages)
The university has an Internationalization Board specializing in the search for opportunities and accomplishing internationalization projects for students and teachers. In addition, it counts on the support of PUC Idiomas (PUCPR language school) to help in internationalization.
Program Magazine with international recognition and foreign participation
The Economic and Socio-environmental Law Magazine, promoted by the GPL, was evaluated in the 2013/2016 quadrennium with Qualis A2, which grants it international impact recognition. The magazine publishes at least 20% of foreign researchers’ studies in English, French, Spanish, and Italian in each issue.
- 2001 – DEVELOPMENT OF A BUSINESS MANAGEMENT EVALUATION INDEX: A METHODOLOGICAL PROPOSAL
- 2001 – VIABILITY INDICATORS FOR SMALL ENTERPRISES
- 2002 – IMPACT OF CONTROL SYSTEMS ON THE IMPLEMENTATION OF A PROCESS STRATEGY
- 2003 – STRATEGY AND PERFORMANCE
- 2006 – MARKETING PERFORMANCE AND PRODUCTIVITY: BEHAVIORAL AND FINANCIAL ASPECTS
- 2007 – CHARACTERISTICS AND DEVELOPMENT OF COMPANIES IN THE SERVICES SECTOR
- 2008 – STRATEGY, SKILLS, AND PEOPLE MANAGEMENT
- 2009 – ADMINISTRATION EPISTEMOLOGY: CHARACTERIZATION OF ADMINISTRATION AS A SCIENCE
- 2012 – STRATEGY, ORGANIZATIONAL NETWORKS, AND COOPERATIVE BEHAVIOR
- 2011 – THE IMPACT OF EMOTIONS ON FINANCIAL DECISION-MAKING
- 2011 – COMMUNICATION EFFECTS ON CONSUMER ATTITUDES
- 2012 – EFFECTS OF HEURISTICS/BIASES IN EVALUATIONS/JUDGMENTS
- 2012 – SOCIAL MANAGEMENT 013 – CORPORATE FINANCE.
- 2013 – AXIS PROJECT: EMPIRICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL APPROACHES IN FINANCE
- 2013 – GAME THEORY APPLIED TO STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
- 2014 – (CNPQ NOTICE – 14/2014 – UNIVERSAL) SOCIAL NETWORKS FOR INNOVATION IN SMALL- AND MEDIUM-SIZED COMPANIES
- 2014 – STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT AND COOPERATIVE GOVERNANCE
- 2014 – COMMUNICATION AND BRANDING
- 2015 – (MCTI/CNPQ NOTICE 25/2015) – APPLIED HUMAN, SOCIAL, AND SOCIAL SCIENCES INTRAORGANIZATIONAL NETWORKS AND STRESS: AN EXAMINATION OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SOCIOMETRIC AND SALIVARY CORTISOL INDICATORS
- 2015 – CLUSTER MAPPING AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF PUBLIC POLICIES FOR INCREASING COMPETITIVENESS AND REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT
- 2015 – (CNPQ / MCTI Nº 25/2015) HUMAN, SOCIAL SCIENCES, AND APPLIED SOCIAL EFFECT OF COMPETITIVE INTENSITY AND TYPE OF PRODUCT ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN SERVICE GUIDELINES AND PERFORMANCE: AN EVALUATION IN BRAZILIAN RETAIL
- 2015 – STRATEGY IMPLEMENTATION IN THE ORGANIZATION: THE IDENTIFICATION AND LOGIC OF THE VERTICAL AND HORIZONTAL ORGANIZATIONAL DETERMINANTS FOR CREATING SYNERGY, VALUE, AND ADVANTAGE.
- 2015 – THE DISPOSITION EFFECT DETERMINANTS: AN EXPERIMENT WITH STUDENTS AND INVESTORS (CNPQ, PROCESS: 306331/2014-4)
- 2015 – SOCIAL INNOVATION AND INNOVATIVITY IN BRAZILIAN COOPERATIVES
- 2016 – (UNIVERSAL CALL NOTICE 01/2016): INTRAORGANIZATIONAL NETWORKS AND SUBJECTIVITY: EXAMINING DUAL IDENTITY RELATIONSHIPS
- 2016 – INSTITUTIONAL LOGIC AND ENTREPRENEURIAL UNIVERSITY EDUCATION
- 2017 – (MCTI/CNPQ NOTICE 311796/2016-8 PRODUCTIVITY SCHOLARSHIP): SOCIAL CAPITAL IN INTRAORGANIZATIONAL NETWORKS AND ATTITUDINAL AND BEHAVIORAL INCOME
- 2017 – ECONOMY APPLIED TO BUSINESS MANAGEMENT
- 2017 – COOPERATIVISM: BRAND VALUE
- 2017 – INNOVATIVITY, INNOVATION, AND PERFORMANCE IN BRAZILIAN ORGANIZATIONS
- 2017 – THE MANAGEMENT OF STRATEGIC ALLIANCES AND THE SUPPLY CHAIN IN THE BRAZILIAN CINEMA
- 2017 – STRATEGIC ADMINISTRATION IN PUBLIC ADMINISTRATION
- 2017 – NEGATIVE DIMENSIONS IN CONSUMER AND BRAND RELATIONSHIP
- 2017 – DIGITAL BRAND REPUTATION
- 2017 – ASSET PRICING
- 2017 – CORPORATE FINANCE
- 2018 – EMPOWERING AGENTS OF CHANGE: SOCIAL ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND INNOVATION IN THE CITIZEN SECTOR (SE-HUB)
- 2018 – CONSEQUENCES OF BRAND ACTIVIST POSITIONING
- 2018 – CONSUMER–BRAND RELATIONSHIPS AND DIGITAL INFLUENCERS
- 2018 – COST-EFFECTIVENESS IN HEALTH
- 2018 – SUSTAINABILITY IN SPECIFIC SECTORS: GOVERNANCE, PROCESSES, AND MANAGEMENT
- 2018 – IMPROVISATION IN ACADEMIC MANAGEMENT: PRACTICES AND ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE (COORDINATOR: VITOR MEYER JR. – CNPQ – UNIVERSAL CALL MCTIC/CNPQ Nº 28/2018 – UNIVERSAL)
- 2018 – THE IMPLICATIONS OF COMPLEXITY AND RELATIONAL GOVERNANCE IN THE EFFECTIVENESS OF MANAGEMENT PRACTICES IN PUBLIC POLICY NETWORKS (COORDINATOR: LUCILAINE PASCUCI – CNPQ – UNIVERSAL CALL MCTIC/CNPQ Nº 28/2018 – UNIVERSAL)
- 2019 – IMPLICATIONS OF COMPLEXITY AND RELATIONAL GOVERNANCE IN PRACTICES ADOPTED IN PUBLIC POLICIES (COORDINATOR: LUCILAINE PASCUCI – FINANCE: FAPES NOTICE NO 21/2018
- 2019 – RELIGIOUS ORGANIZATIONS
Faculty
Alceu Souza
PhD in Business Administration, 1996, EAESP at Getúlio Vargas Foundation, São Paulo, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: financial viability of projects and strategic cost management. Research group: decision processes (DP).
Angela Cristiane Santos Póvoa
PhD in Business Administration, 2013, Mackenzie Presbyterian University, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: behavior economy, economy, finance, corporate sustainability, and strategic management. Research group: sustainability in organizations (GPSO).
Bruno Henrique Rocha Fernandes
PhD in Business Administration for faculty of economics and administration, University of São Paulo (FEA-USP), Brazil. Sandwich PhD, Cambridge University. Preferred areas of research: strategic people management, strategy and competitiveness, and organizational studies.
Carlos Olavo Quandt
PhD in Urban and Regional Planning, 1993, University of California at Los Angeles, United States. Preferred areas of research: Knowledge Economy and Innovation. Research group: knowledge and innovation information management (GCI).
Eduardo Damião da Silva
PhD in Administration Sciences, 2001, ESADE at Universidad Ramon Llull, Barcelona, Spain. Preferred areas of research: business strategy, corporate strategy, scenario development, and strategic cost management. Research group: GPAE.
Eliane Cristine Francisco Maffezzolli
PhD in Administration, 2010, UFPR, Curitiba, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: marketing and consumer behavior. Research group: Marketing - Consumer Behavior (MKT).
Heitor Takashi Kato
PhD in Business Administration, 1998, at EAESP at Getúlio Vargas Foundation, São Paulo, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: strategy, marketing, and econometrics. Research group: GPAE and MKT.
Jansen Maia Del Corso
PhD in Administration Sciences, 2002, at ESADE at the Universidad Ramon Llull, Barcelona, Spain. Preferred areas of research: management and strategic planning and organizational modeling. Research group: GPAE.
Juan José Camou Viacava
PhD in Administration at the UFPR, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: consumer behavior, digital marketing, and marketing strategy.
June Allison Westarb Cruz
PhD in Administration, 2012, PUCPR, Curitiba, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: corporate finance, network analysis, and cost management. Research group: GCI and DP.
Paulo de Paula Baptista
PhD in Business Administration at USP. Consultant in marketing and strategy, who has participated in projects of companies of national prominence in the sectors of electricity, telephony, supermarket retail, food industry, civil construction, and agribusiness. He has taken courses at Harvard University to improve the research in competitiveness microeconomics. He has been working for more than 10 years in the master's and doctorate programs. He is the Director of Planning and Development and the Administrative Vice President at PUCPR, being the executive responsible for consolidating the university's strategic, budgetary, infrastructural, marketing, and relationship planning.
Paulo Otávio Mussi Augusto
PhD in Business Administration, 2006, EAESP at Getúlio Vargas Foundation, São Paulo, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: business strategy, theory of organizations, strategic practice, and institutional analysis. Research group: GPAE.
Pedro Guilherme Ribeiro Piccoli
PhD in Administration at the PUCPR, Brazil. Sandwich PhD, McGill University. Preferred areas of research: corporate finance, behavioral finance, and decision making.
Renato Zancan Marchetti
PhD in Sciences de Gestion, 1991, École des Hautes Études Commerciales (HEC-Paris). Preferred areas of research: marketing strategy, consumer behavior, and diffusion of innovations. Research group: MKT.
Ubiratã Tortato
PhD in Production Engineering, 2006, Polytechnic School of the University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil. Preferred areas of research: sustainability, sustainable chains, and logistics. Research group: GPSO. Research preferences in 2016: eco-efficiency and sustainable universities.
Victor Meyer Júnior
PhD in University Administration, 1982, University of Houston (United States). Preferred areas of research: strategy in complex organizations, complexity and organizational management, and strategic management in nonprofit organizations. Research group: GPAE.
Courses
Strategy: An Institutional Approach
Goals
The course’s general goal is to contribute to the improvement of students’ analytical capacity by discussing the concepts of institutional theory, especially those disseminated in sociology, which attempt to clarify the formulation, maintenance, and change of strategies in organizations. Specifically, it is intended to (1) distinguish the origin and development of institutional theory and, above all, its sociological aspects; (2) understand the propositions and concepts of institutional theory that guide the explanation of institutions’ effects and the processes of institutionalization in the implementation and transformation of organizational strategies; and (3) identify the purpose and importance of adopting such propositions and concepts for their study and application within organizations.
Methodology
This course’s content will be taught through didactic resources with lectures on the program topics and discussion of texts recommended for reading, and an evaluation system. Considering the emphasis on student involvement in teaching activities, the evaluation will be conducted based on the following criteria: attendance; class preparation, verified through participation in group discussions; group discussions with the professor in at least one class during the quarter by choosing the material, formulating questions and acting as a facilitator, performing extra-class individual work.
Strategic retail and services management
Goals
Provide the students with an insight into theories in the areas of services and retail within the area of marketing
Summary
- Origin of the interest for studies in the sector
- Characteristics of services companies
- Aspects of sector demand
- Production of services
- Perception of services
- Characteristics of retail companies
- Aspects of a retail location
- Selection and presentation of products
- Retail organization
Quantitative Data Analysis I
Goals
In general, the Quantitative Data Analysis I course aims to familiarize students of the graduate (master’s) program in administration with the different statistical methodologies so that the student can have better foundations with statistical tools, obtaining greater support for articles and dissertations developed in the program.
Summary
- Parametric Hypothesis Tests: Normal and Student’s t
- Test for the difference in the means of two populations
- Variance Analysis for a factor
- Sheffé and Tukey tests
- Non-parametric tests:
- Chi-square
- Sign test
- Kruskal-Wallis test
- Kolmogorov-Smirnov test
- Normal Probability Graphs
- Linear Correlation between Variables
- Simple and Multiple Linear Regression: Estimation, interpretation, and significance of parameters
Quantitative Data Analysis II
Goals
Its main goal is to teach the students in the PPAD about the main multivariate statistical techniques, mainly focusing on their different applications in the applied social sciences. Based on the analysis of theses and dissertations and scientific articles, it aims to study the methodological and statistical aspects of the development of scientific research. It is also intended to conduct practice classes for students to understand how to use the SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) computer package and Statistical for Windows to conduct research in business administration.
Summary
- Data preparation; similarity, and dissimilarity measures
- Factor analysis: factor derivation, number of factors, and interpretation of factors
- Conglomerate analysis (Clustering): derivation and analysis
- Multiple linear regression analysis
- Analysis of variance for more than one factor
- Discriminant analysis
- Logistic regression
Complexity and Organizational Management
Goals
The course goals are as follows: (1) Analyze the current context and its management challenges. The topics to be examined include the following: organizational complexity and its managerial implications, organizational management and changes in the business environment of organizations, and emerging management models concerning emerging organizational models in the Knowledge Era. (2) Develop a critical view of management models and changes in the context of corporate business, examine the applicability of new management models in the Brazilian context, and encourage participants to reflect on the current context, its challenges, and the practice of new management models in the knowledge society.
Summary
Part I: Analysis of the current business context
- Megatrends and global paradoxes: Impact on organizations
- The evolution of the Pre-Industrial to Industrial and Post-Industrial Society
- The Knowledge Society: The Age of Intellectual Capital
Part II: Organizational complexity
- Organizational characteristics and organizational complexity
- Chaos and complexity theories
- Organizations as complex systems
- Complexity and organizational management
Part III: Business management models
- Traditional management models
- The emergence of new business management models
Part IV: Emerging management models in the knowledge society
- Knowledge management as a management model
- The virtual organization: the horizontal organization based on partnership relations and information technology
- The horizontal organization (integrated process management)
- The new inter-company relationships (networks)
- The concept of transnationals or organizations without borders
- Other emerging forms of organization
- The organizational metaphors
Part V: The impact of emerging management models on organizations and people
- New context: changes and innovations in organizations
- Impact on the organization
- Impact on people
- Implications of environmental challenges and organizational complexity in the management of organizations at present.
Consumer Behavior
Goals
The course’s goal is to analyze the factors that allow the understanding of consumers’ buying behavior and their implications in the formulation of an organization’s strategy, especially in marketing policies. The course discusses the main perspectives of consumer analysis involving socio-cultural aspects, individual differences, and the purchasing decision process stages.
Summary
Perspectives for analyzing consumer behavior. The determinants of a functional problem-solving process: the degree of involvement. The purchasing decision process stages and the marketing strategy: recognition of the problem, search for information, evaluation of alternatives, purchasing decision, and satisfaction. Interpersonal influences: reference groups and the purchase decision in the family. Sociocultural influences: social class, lifestyle, and culture.
Econometrics Applied to Time Series
Goals
In general, the Econometrics Applied to Time Series course aims to familiarize students from the Graduate Program (Master’s/Doctorate) in Administration with the different econometric methodologies so that they have a basis of econometric tools when modeling economic phenomena, thus providing more significant support in the development of articles, theses, and dissertations in the program.
Summary
- Simple Linear Regression Model
- Multiple Linear Regression Model
- Multi-collinearity
- Autocorrelation and Heteroscedasticity
- Dummy variables models
- ARIMA and ARIMA Modeling with Intervention
- Dynamic Modeling
- Unitary Root
- Cointegration between variables
- Autoregressive Vector Modeling.
Knowledge Economy
Goals
This course’s goal is to (1) introduce the economic aspects of information and innovation and to understand the impacts of the knowledge-based economy, (2) analyze the competitive environment using microeconomics elements (knowledge-intensive goods and services, and innovation process) and macroeconomics (knowledge economy and innovation systems), and (3) apply information technology and information management to formulate strategies and enhance the value of knowledge.
Summary
- Introduction – Basic concepts: information and knowledge economy. Tangible and intangible investments.
- Knowledge management and knowledge economy – Market mechanism. Externalities. The limitations of economic models.
- Globalization and Brazilian insertion in the knowledge economy. Capital mobility; information, goods, and services; global competitiveness of products; and people.
- Technology and productivity. New structures of production, distribution, and consumption.
- Network Economy. Strategic networks and alliances, and cooperation agreements. Modularization of companies and infrastructure.
- Innovation and IM. Knowledge codification and innovation location. Support structures. Regional and national innovation systems, and clusters
- Work, learning, and intangible assets. Human capital and learning as the essence of development. Estimates of value, trade, and investment in intangibles.
Strategy and Business Policies
Goals
This course aims to provide students with a critical view of the main theories and trends in business strategy; develop skills to assess, critique, and contribute to the literature on strategy formulation; and develop creative ideas by producing a publishable article.
Summary
- Business strategy concepts and models.
- Main trends in the study of business strategy, analyzed comparatively.
- Competitive advantage.
- Education models and maintenance of competitive advantage.
- Economic and organizational schools.
- External environment analysis.
- Contextual, transactional environment and instability models.
- Industry Analysis.
- SCP analysis and positioning.
- Value chains and constellations.
- Variants, clusters, and linear value chains.
- Strategic alliances.
- Typology and classification. Comparative performance analysis.
- Resources and skills analysis.
- Comparison with traditional theories of industrial positioning.
Strategy in Functional Areas
Goals
The goals are to provide students with a more focused view of strategies and concerns at the level of a company’s functional areas and analyze the interrelationships between the various such areas and a more integrated view of these areas.
Summary
- Functional strategies.
- Production and operations strategies.
- Finance strategies.
- Purchasing and materials strategies.
- Research and development strategies.
- Information systems strategy.
- Human resource strategies.
- Marketing strategies.
Strategies and Marketing Analysis
Goals
This seminar aims to analyze the main perspectives on the creation of a marketing strategy in an organization and enable the participant to understand the theories and models that form the foundations of a marketing strategy.
Summary
- The marketing process in a company and society.
- Managing market orientation in a changing environment.
- Market structure, competition, and competitive advantage.
- The customer’s response behavior.
- Knowledge and marketing information in the organization.
- The formulation of the marketing strategy.
- Marketing strategy through relationships and organizational networks.
- Strategic brand decisions. Strategic innovation decisions and new products.
- Evaluation of marketing performance.
Ethics and Science Philosophy
Goals
This course aims to present the philosophical way of analyzing and facing problems as an enrichment factor for reflection on the various areas of knowledge and performance. The goal is to provide students with a perspective on the theoretical and methodological assumptions inherent to the understanding/knowledge of the various sciences and areas of knowledge. The course also aims to offer ethical evaluation criteria, through different perspectives and conceptions, allowing the student to analyze the implications of the knowledge he/she generates and the actions he/she develops. Finally, the course presents the conditions of the emergence of the type of moral valuation that we currently have, as an instrument to optimize the practice of ethics while reflecting on human actions.
Summary
- Ethical debate in a globalized society.
- The moral conscience.
- Ethics, law, and morals.
- The ethical models of Western thought.
- Some aspects of ethical concerns in companies.
- The construction of sciences: a brief history.
- The knowledge paradigms.
- Human and social sciences and power relations.
Brand Management
Goals
Critically approach the central topics of communication and brand management, allowing participants to understand the main factors that determine brands’ performance and value.
Summary
- Definitions, importance, and function of brands
- Brand identity and positioning
- Brand elements
- Brand value and brand equity determinants
- Architecture and brand portfolio
- Brand extension
- Name changes and brand mergers
- Decline and revitalization of brands
- Brand loyalty
- Global brand expansion
- Measuring brand value
Methodology
This course’s content will be taught through lectures, text discussions recommended for reading, seminars held by the participants, and individual and group exercises.
Evaluation System
Evaluation will be based on students’ participation in the classroom, the work they prepare and present throughout the course, and the quality of the academic article they deliver at the end of the course.
Strategic IM
Goals
Introduction to the main concepts related to the innovation process and IM practices, in the context of strategic administration.
Discussion of the strategic importance of technological and organizational innovation in different contexts.
Analysis of the components of an IM model in the context of its implementation in specific cases.
Summary
- Contextualization: concepts and definitions; innovation as a strategic option that makes organizations competitive, particularly those with a technological base.
- IM: management practices and processes; the changes that organizations implement in response to different contingencies.
- Innovation strategies: main components of a corporate strategy focused on innovation, incrementalist, and rationalist approaches.
- The context of innovation: how organizations analyze the competitive environment in which they operate and the local, regional, and national innovation environment; policies.
- IM Model: the choice of technological trajectories; integration to create a favorable learning environment.
- Implementation and case studies: discussion of the main elements that lead to the implementation of IM.
Strategic Cost Management
Goals
In general, the Strategic Cost Management course aims to familiarize students with the main costing methods and the possible management analyses derived from these methods, and discuss the relevance of the information generated by these methods to support business strategies. This course’s specific goals are to understand the process of accumulating costs for products and services, identify the main costing methods and their potential, and recognize the importance of cost information for decision-making.
Summary
- Introduction.
- Basic concepts.
- Cost classification.
- Aggregation levels for product costs.
- Objectives of cost calculation, cost management, and strategic cost management.
- The economic concept of profit.
- Concept of added economic value.
- Production costs.
- Absorption costing.
- Costs of idleness and process inefficiency.
- Management analysis in absorption costing.
- Direct costing.
- Cost–volume–profit analysis.
- Constraints Theory
- ABC costing.
- Trends.
Research Methodology Applied to Administration I
Goals
Provide resources for students to conduct and evaluate scientific research, expanding their knowledge of scientific methods and language, stages of scientific research, types of research, population and sample, data collection procedures, and data analysis techniques.
Summary
- Nature of science and characteristics of the scientific method
- Taxonomy of research types
- Research project importance and stages
- General guidelines for choosing a topic
- Research problem formulation and goal definition
- Construction of theoretical-empirical basis
- Choosing variables and elaborating questions or research hypotheses
- Mensuration, measurement scales, and indicator construction
- Development of data collection instrument
- Data collection approaches
- Validity and reliability
- Population and sampling
- Introduction to data analysis techniques
- Writing research reports.
Research Methodology Applied to Administration II
Goals
The course’s general goal is to provide analytical and methodological resources that allow students to evaluate and conduct research in administration, particularly their doctoral dissertation. At a specific level, it is intended to lead the doctoral student to a more comprehensive view of the construction of theories and their role in the generation of knowledge in administration. Further, the course aims to deepen the understanding of the bases and methodological delimitation of scientific research and identify the preparation and writing process stages of scientific research, especially the qualification project and the doctoral dissertation.
Summary
- Theory construction: conceptions about theory; acceptability criteria – internal and external consistency, operability, generality, theory, and practice.
- Data collection: advanced notions about measurement – operational definition, validity, reliability, trustworthiness, and measurement scales.
- Data analysis: relationships, inferences, interpretations, refutation, sources, and data collection instruments (interview, questionnaire, observation, etc.); data, reference frame, and analysis.
- The dichotomy between qualitative and quantitative research.
- Experimental, quasi-experimental, and non-experimental research.
- Multi-method and multilevel analyses.
- Longitudinal analysis.
- Steps in scientific research preparation and writing, the qualification project, and the doctoral dissertation.
Qualitative Methods
Goals
The course goal is to deepen the discussion on the use of qualitative research in the social sciences and especially in administration. The course aims to help students gain knowledge that allows them to identify when a research problem requires using a qualitative approach, exclusively or combined with quantitative methods. It also aims to prepare students to apply qualitative techniques and analyze the data they collect.
Summary
- qualitative methods
- Ethnography
- Interviews
- Discourse analysis
- Focus groups
- Observational methods
- Document analysis
- Case studies
- Action research
- Qualitative data analysis
- Quality issues in research
Investment Decision Models: Real Assets
Goals
The main goal is to familiarize students with the main investment analysis methods used in project selection. The course’s specific goals are to help students understand generating project cash flow, analyze projects in the return and risk dimensions, and model the investment decision process.
Summary
- Introduction.
- Basic Concepts.
- Financial mathematics review.
- Financial viability indicators for projects.
- Multi-index method.
- Investment analysis after income tax.
- Effects of funding sources and return on equity.
- Investment analysis under risk and uncertainty.
- Simulation of random cash flows using Excel.
- Markovitz model for composing portfolios.
- CAPM model for project selection.
- Real options theory; Trends.
International Businesses and Corporate Strategy
Goals
Provide students with an insight into the main aspects of a company’s operating environments in an international context. Provide the student with an impact assessment in terms of strategic and organizational decisions in a global environment.
Summary
- The global economic environment
- Competitive advantage of companies
- The Porter diamond model
- Analysis of potential markets
- Entry strategies
- Competitive strategies
- Cooperative strategies
- Global strategies
Strategic Planning and Organizational Modeling
Goals
Discuss the organizational diagnosis process
Know and debate relevance analysis as a process applied in organizational strategic decisions
Discuss organizational strategy
Discuss, understand, and evaluate the importance of cultural and political influences and mechanisms for direct strategic change in these systems
Understand the strategic planning and preparation process and organizational modeling for their implementation and control.
Summary
- Planning as a strategy-sensitive agent
- Strategic management versus strategic planning
- Organizational change
- Middle management as an anchor of the decision-making process on the direction, modeling, and implementation of strategies and result achievement
- Structure within a strategic context
- Strategic control.
Pedagogical Processes in Higher Education
Goals
By taking the teaching process as a study goal from the university professor, and given the context of his/her pedagogical practice, conduct a critical analysis of this practice and propose innovative projects in the different fields of higher education.
Based on the society and problematization of the pedagogical practice developed in higher education institutions, critically analyze the multiple aspects of the teaching process, historicizing and explaining its theoretical and methodological assumptions.
Understand the different approaches to the content–form relationship of the teaching process in the context of the historical circumstances in which they are produced.
Based on the operational components of teaching techniques, discuss the methods’ epistemological assumptions in the context of the theories that underlie them.
Experience, analyze, and systematize the teaching proposal in a content–form relationship and collectively systematize knowledge.
Summary
- University pedagogy. Teaching process: Contributions of great pedagogical doctrines: foundations and didactic elements.
- The university course:
- Teaching and its relations: content–form, professor and student, and researcher–teaching–society.
- Innovative teaching projects: fundamentals, didactic elements, possibilities, and limits.
Information Systems: Indicators of Strategic Controls
Goals
The student will be able to identify, understand, analyze, and indicate solutions to information problems in the business environment, to support decision-making concerning strategic organizational planning by using performance indicators.
Summary
- Information systems fundamentals.
- Identification of information problems.
- Troubleshooting information.
- Information systems to create strategic organizational performance indicators.
Strategy as Practice – A Practical Perspective in Strategy
Goals
The course’s goal is to deepen the discussion on strategy as a social practice. By focusing on strategy, one can identify the strategy praxis, its practitioners, and the different practices used to build a systematic view of the strategy field. The course adopts a sociological approach to the field’s construction, mostly linked to the social practice theory. As a secondary goal, it discusses and analyzes the dualisms currently present in the strategy field: process and content, environment, and organization; planned and emerging strategy.
Summary
- Strategy as practice
- Social action and social practice
- Action theory
- Building social actors in strategy (strategy practitioners)
- Strategic discourse and narratives
- Strategy micro-processes
- Strategizing
- Strategy field tools, concepts, and language
- Overcoming the field’s dualisms
Theory of Organizations
Goals
The course’s general goal is to provide theoretical and empirical instruments that will allow the student to become familiar with the conceptual universe of organizational theory and, thus, develop the ability to analyze organizations. Specifically, it is intended for students to understand the main concepts and theories that guide the analysis of the various dimensions of organizations and verify the purpose and relevance of considering such dimensions for research in the field of administration and practice in organizations.
Summary
- Emergence and evolution of the theory of organizations.
- Bureaucratic organization: origin, essential characteristics, ideal type, functions and dysfunctions, unidimensionality, and multidimensionality.
- Structure and technology in organizations.
- Power, control, and conflict in organizations.
- Change and innovation.
- Organizations and the environment.
- Culture and organizational identity.
- New organizational forms.
More Information
MASTER’S PROGRAM
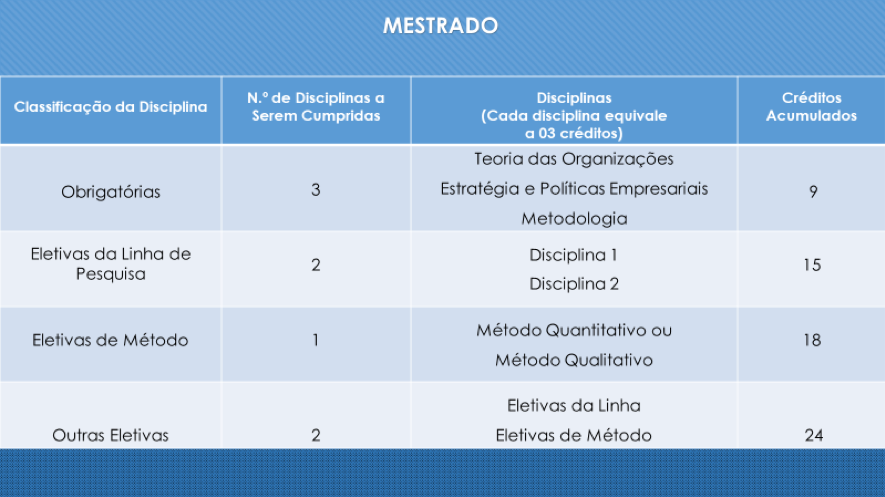
The Master’s Program at PUCPR comprises two stages: the curricular and monographic stages. The curricular stage consists of the first two semesters, in which students must complete a minimum of 24 credits in courses. The monographic phase corresponds to six credits. Thus, the total number of credits for the completion of the Master’s program is at least 30 credits. In the monographic phase, the student elaborates and defends his/her thesis.
The curriculum of the Master’s Program in Administration at PUCPR provides courses for the completion of compulsory and elective courses and the preparation and defense of the thesis.
To obtain the Master’s in Business Administration degree, the student must fulfill at least 30 credits, 24 of which are obtained in the curricular phase and must be achieved as follows:
Three) courses must belong to the mandatory group, totaling nine credits;
At least two elective courses must belong to the research line to which the student is linked. The line of electives courses adds up to six more credits.
At least one course must be from the instrumental core, of a quantitative or qualitative nature, depending on the research project, adding three more credits;
Thus, 18 credits must be fulfilled according to the proposed structure. The remaining credits can be fulfilled through other courses from any nucleus or through activities proposed by the Program that allow the fulfillment of credits, such as participation in research seminars and publication of qualified articles, whose number of credits depends on the impact factor of the publication.
Please check whether this change retains your intended meaning here.
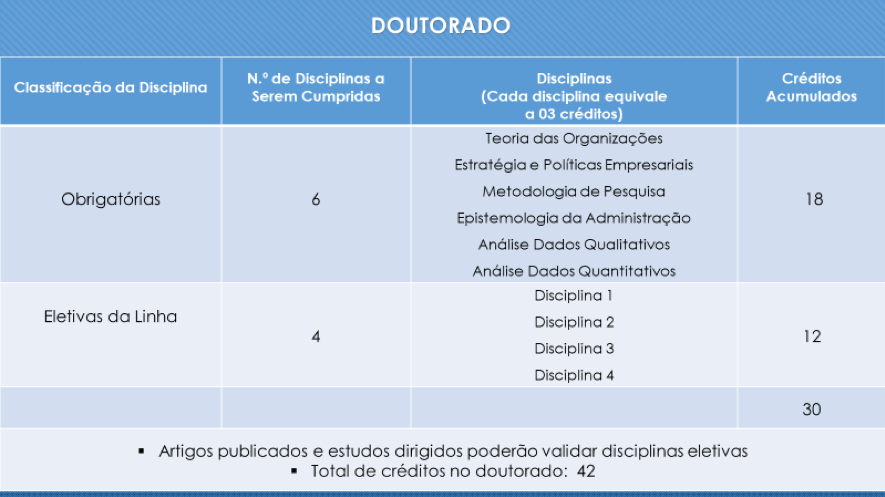
DOCTORAL PROGRAM
The Doctoral Program comprises two phases: the curricular phase and the monographic phase. The curricular phase consists of the first eighteen months, during which students must complete a minimum of 30 credits. The monographic phase comprises the completion of the remaining 12 credits, which generally occurs between the 18th and 48th month of the program. Thus, the total number of credits for the completion of the Doctorate is at least 42 credits.
PPAD is one of the leading research programs in the Paraná region, responsible for the education of a relevant contingent of professors who work inside and outside the region. Approximately 400 master’s and more than 90 doctoral students have graduated throughout PPAD’s history, making the region a vital professor education area. In addition, its performance in the market allows for a closer relationship between companies and academia.
PPAD professors also work in specialization programs, extensions, companies, and offer consultancy to impact the society in which they work.
In addition, PUCPR offers tuition-free scholarships for students whose advisors have projects approved by national or foreign development institutions or who are scholarship productivity holders. For such students, PUCPR pays for participation in national or foreign conventions.
PPAD’s actions create benefits for society. Among these actions are the development of research by master’s and doctoral students who seek to provide answers to problems present in organizations, as well as the development of research focused on emerging social themes, searching for diagnoses, and proposing scientific solutions. Institutional representations in conferences, forums, and public and private institutions are focused on developing solutions applied to society, especially to the most economically vulnerable audiences. Among the main areas of research with social impact, the learning and development process, and institutional representations are the following: the unified health system, higher and basic Education, solidarity economy, and social projects.
Since 2011, PUCPR has engaged in a project called Excellence in Stricto Sensu that is aimed at internationalizing the institution’s programs to achieve maximum scores of 6 and 7 and to promote transdisciplinarity and innovation in different areas of knowledge, especially in its strategic areas. The PIBIC master program is one its greatest differentials (it allows talented students to attend both undergraduate and graduate stricto sensu programs and develop part of their research in a highly qualified foreign institution) as well as being in harmony with society and focusing on innovation.
The institution must also be constantly attentive to the changing needs of the society, with alignment/realignment to the CAPES criteria and oriented to develop internationally, having internationalization as its main guide in the search for quality in teaching and research.
Every graduate program must meet the criteria set by their corresponding committee; therefore, each program strategic planning and operating criteria needs to be done accordingly.
Criteria for each area need to be discussed within the program annually so that all necessary and appropriate corrective actions can be taken during the four-year period. Each program is committed to structuring and readjusting its strategic planning annually in search of excellence. In addition, the programs are encouraged to rethink their lines of research in order to adapt to the rapid changes that may occur in international and national scenarios.
This graduate program’s dynamism and flexibility must always meet quality criterion both in master’s and doctoral training and in the development of research and innovation, essentially aiming at the improvement of society. Thus, an annual review of each program strategic planning is requested that contains the topics below at a minimum:
- i. Mission and vision of the program;
- ii. Summarized annual opinion produced by an external evaluator; the annual evaluation by an external member is an institutional practice conducted since 2006, which allows for the annual performance of each program to be assessed according to the area criteria;
- iii. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and risks (preparation of a SWOT matrix showing external and internal factors) considering the goals for the current and next four years;
- iv. Goals (measurable objectives) established for the consolidation and development of strengths and improvement of weaknesses;
- v. Actions (processes) necessary to achieve the objectives, people in charge, and monitoring instruments; in this topic, the coordinator and the institution should get involved to consider resizing the faculty and the student body, criteria for accreditation/re-accreditation, infrastructure, selection process, strategies to increase fundraising, and citations and innovation, among other items;
- vi. Preliminary text of the program’s self-assessment describing the last four years containing at least the following information: stages of the self-assessment process; analysis of results and achievement of objectives; necessary actions for its consolidation and internationalization;
The IDP (Institutional Development Plan) document presents the strategic plans of all the programs aligned with the institutional planning, containing the Mission, Vision, SWOT Matrix, Canvas, and road map, and providing information on the needs and intentions of the programs for the 2017–2020 and 2021–2024 quadrennium of the CAPES evaluation.